

Ø Endospores contain high amount of dipicolinic acid in its core (protoplast). Some of the possible explanations are given below: Several explanations are now prevailing in the scientific community to explain this.
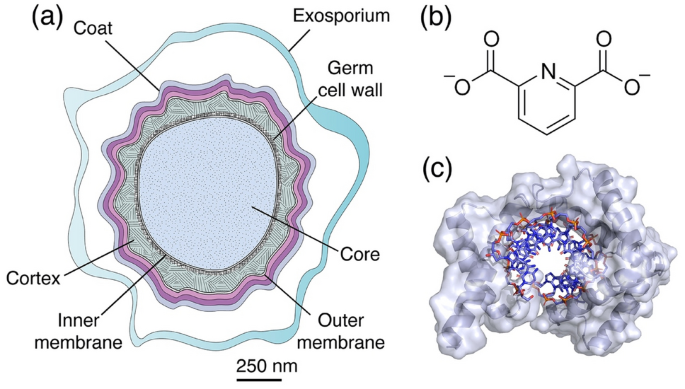
The exact reason for the high resistance of endospores towards extreme temperature, radiation and chemicals is still unknown. Why the Bacterial Endospores are Extremely Resistant to Temperature, Radiations and Chemicals? Ø The core only contains about 10 – 25% of water of the normal vegetative cell. Ø Unlike the vegetative cells, the core protoplast is metabolically inactive. Ø The core contains ribosomes and centrally placed nucleoid (genetic material). Ø The endospore core has a normal cell structure as that of a vegetative cell. Ø Spore cell wall covers the central protoplast or Core of the endospore. Ø The innermost layer of the spore is called the Spore Cell wall or Core Cell Wall. Ø The peptidoglycan in the cortex is less cross linked than that of vegetative cells. Ø The cortex is composed of peptidoglycan Ø Cortex is very large and sometimes occupy as much as half of the spore volume. Ø Cortex is the thicker wall layer in the endospores. Ø The thickness of the spore coat is one reason for the high resistance of endospores towards heat, radiation and chemicals. Ø Beneath the exosporium is a Spore Coat composed of several layers of proteins. Ø The outermost layer of the spore is called exosporium which is relatively thin and delicate. Ø The structure of endospore is very complex since they possess multilayered coverings. Learn more: Comparison of Archaea, Bacteria and Eukarya Learn more: Difference between Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria Ø No Archaebacteria are known to produce endospores.īacillus: vegetative cells (pink) and Endospores (green) ( Image Source CC Wikipedia) Ø Both aerobic and anaerobic bacteria (of Gram-positive type) can produce endospores. Ø Based on the position of spores, the sporangium/spores may be Central spore, Sub-terminal spore, Terminal spore or Terminal spore with swollen sporangium. Ø The position of the endospore within the spore mother cell also varies.
Ø These characteristics are used for the identification purpose in bacterial taxonomy. Ø Sporangium shows distinct differences from other vegetative cells. Ø The endospore-producing mother cell is called sporangium. Ø The classically used stain to visualize endospore is Malachite Green and the staining procedure is known as Schaeffer–Fulton Staining. Ø Specific stains and special staining techniques are required to stain the endospores. Ø Endospores will NOT take the usual bacterial stains such a safranin used in Gram-staining. Ø Endospores can be visualized under light and electron microscope. Ø However, endospores can be killed by autoclaving (at 121 oC).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
